
Sarah was unable to explain why the smell of diesel fuel made her heart race. She was just 34. The combat veteran found herself avoiding gas stations. No one was able to understand her strange excuses to skip family road trips. Well, sometimes, she woke up drenched in sweat. Because of nightmares, she could not quite remember.
Her close ones suggested she "just move on." Her family wondered why she seemed so distant. Even Sarah questioned herself: "Why can't I just get over it?"
But Sarah was not being dramatic, and she was not weak. What she was experiencing was Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)... a serious mental health condition that affects millions yet remains profoundly misunderstood.
That was definitely not about her being "stressed out" or having bad memories. PTSD or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a medical condition. It is included in DSM-5, Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders. It has biological roots that fundamentally change how the brain processes threat and safety. And most importantly, it is treatable!!

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental condition that develops after someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. Normal stress responses fade with time. But unlike them, the PTSD symptoms persist for months or years. The problem is that they significantly interfere with daily life.
PTSD affects approximately 6% of the U.S. population at some point in their lives. According to the NIH report, women are twice as likely as men to develop PTSD. The APA (American Psychological Association) reports the lifetime prevalence rates of PTSD. They are around 10% to 12% in women. While in men it is about 5% to 6% only..
The condition, or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder symptom, can develop after various traumatic experiences.
Such as:
It is totally a misconception that your Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is not a sign of weakness, or character flaw, or inability to cope. PTSD is a psychiatric condition. It is linked to neurobiological changes in the brain. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder requires proper treatment, just like any other medical illness.
Each person suffers from different symptoms and triggers of PTSD. However, mental health professionals organize PTSD symptoms into four main categories.
Let's understand these clusters. It will help you clarify how Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder manifests. And why is it so disruptive for you or anyone!
What does it mean? It means that the traumatic event keeps intruding into your present life. It may be through unwanted memories, flashbacks, or nightmares.
Common Symptoms:
Examples:
→ A car accident survivor experiences panic every time they hear brakes screeching.
→ A sexual assault survivor has intrusive images that disrupt their concentration at work.
What does it mean? You try every possibility to avoid anything that reminds you of the trauma. And these avoidance and acts severely limit your life.
Common Symptoms:
Examples:
→ Someone assaulted in a parking garage avoids all parking structures, limiting job opportunities
→ A first responder who witnessed a child's death avoids being around children
What does it mean? The trauma fundamentally changes your thinking. There is a huge negative influence on how you see yourself, others, and the world.
Common Symptoms:
Examples:
→ A trauma survivor believes "the world is completely dangerous" and can't feel safe anywhere.
→ Someone experienced betrayal trauma from a business partner. He becomes convinced that "everyone will hurt me".
→ After a mishap in a gathering, a person stops attending social gatherings. He started feeling disconnected, even from close friends.
What does it mean? Your nervous system always stays in "high alert" mode. It constantly keeps scanning for danger even when you are safe.
Common Symptoms:
Examples:
→ In restaurants with friends and family, a veteran sits with their back to the wall, constantly watching the door.
→ A survivor snaps at family members over minor issues, then feels guilty.
→ Someone jumps violently and reacts strangely, unexpectedly. Although he is only touched by his loved ones.
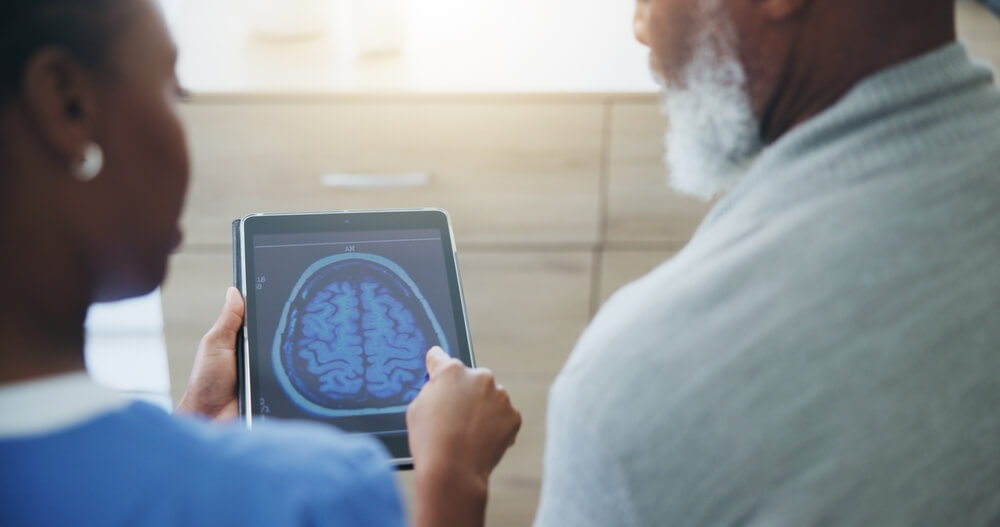
Brain imaging studies reveal specific changes in people with PTSD. The brain's "fear center" (Amygdala) becomes overactive, constantly signaling danger. Hippocampus, the memory center, shows reduced volume. It affects how traumatic memories are processed.
Prefrontal cortex dysfunction is observed. The reasoning center struggles to regulate the fear response. HPA axis; the stress hormone system becomes chronically activated.
They are measurable biological changes. They explain why Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder feels so overwhelming. And they affirm the need and necessity of professional treatment of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder.
Yes, traumatic events are unavoidable. They are part of everyone’s life. And most of them stay in your memory. It is completely normal to experience some distress after any traumatic event.
However, you should consider a professional evaluation if:
→ Symptoms persist for more than a month after the trauma.
→ Symptoms are getting worse rather than better.
→ You are avoiding important areas of your life due to symptoms.
→ You are using alcohol or drugs to cope.
→ You are having thoughts of harming yourself or others.
→ Symptoms are interfering with your work, relationships, or daily activities.
→ You feel like you can't function normally.
→ You are experiencing intense guilt, shame, or self-blame
When Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder goes untreated, its effects ripple through every aspect of your life:
| Physical health consequences of PTSD |
|
| Mental health complications due to PTSD |
|
| Relationship difficulties due to PTSD |
|
| PTSD causing Occupational problems |
|
| PTSD affects Quality of life |
|
The good news? These outcomes are not inevitable. With proper treatment, people with PTSD can recover and reclaim their lives.

Recovery from PTSD does not necessarily mean forgetting what happened. Nor is it about never feeling distressed about it.
Recovery means:
You can observe changes in your symptoms with:
Post-traumatic stress disorder often coexists with other conditions. It requires expert-led, specified treatment and medication management approaches.
Medication responses vary significantly between individuals. So, careful monitoring prevents complications and ensures effectiveness. In many cases, dosing adjustments may be needed as symptoms change, which can only be done safely under expert care.

At Health and Psychiatry, expert mental health care in Florida, we understand that PTSD is not something you can simply "get over" or manage alone. Led by Dr. Sajan Dinar, MD, our Florida practice specializes in comprehensive PTSD treatment that addresses both the psychiatric and holistic aspects of recovery.
Our approach includes:
→ Thorough evaluation to accurately diagnose PTSD and identify co-occurring conditions.
→ Evidence-based medication management when appropriate.
→ Coordination with trauma-focused therapists.
→ Regular monitoring and treatment adjustment.s
→ Family education and support.
→ Long-term maintenance care to prevent relapse.
At Health and Psychiatry, Dr. Sajan Dinar, MD, provides specialized psychiatric evaluation, therapies, mental health care, and medication management according to each person's unique Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder presentation and overall health profile.
Take the first step toward recovery from your Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and lead a happy, trauma-free life!


Copyright © 2024 Health & Psychiatry, All rights reserved