
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a recognized complex neurodevelopmental disorder. It stems from variations in how the brain grows and works. It changes the way the brain thinks, sustains attention, and manages impulses.
If left untreated, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder will interfere with nearly every aspect of life. With proper management, treatment, however, people with ADHD can have normal, productive, and enjoyable lives.
Most importantly. People with Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder can achieve great success in their lives. Only if their condition is understood and managed properly....

The symptoms of ADHD are typically divided into three categories: Inattention, Hyperactivity, and Impulsivity. Each individual has a different type and severity of symptoms.
The way symptoms appear typically changes with age and environment. A young child may rush around the classroom, while an adult may exhibit chronic procrastination and a spotty work history.
Left untreated and unnoticed, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder can lead to disastrous difficulties; problems at school, relationship issues, and even higher risks of injuries and drug abuse.

As research indicates, ADHD occurs as a result of the interaction of some genetic, neurological, or environmental factors.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder can be inherited. Researchers estimate its heritability at 70–90%. Multiple genes (e.g., DRD4, DAT1) that regulate brain chemicals such as dopamine have been identified as associated with ADHD.
Certain conditions are more vulnerable:
According to a national survey of parents, the CDC estimates 7 million (11.4%) U.S. children aged ranging from 3 to 17 years have ever been diagnosed with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder.
However, ADHD does not affect everyone in the same way.
Boys are more likely to be diagnosed. 15% of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder cases are diagnosed in boys and 8% in girls. It may be due to many girls are not diagnosed because their symptoms are less disruptive.
Girls are more likely to have inattentive symptoms like daydreaming or quiet disorganization rather than hyperactivity. Many cope by "masking" their challenges, so diagnosis is delayed.
Numerous adults discover they have Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder just after their child is diagnosed. In grown-ups, ADHD may lead to poor job performance, issues with maintaining relationships, and financial concerns.
Cultural expectations also come into play. In societies where females are meant to be passive and obedient, inattentive ADHD might not be noticed for many years.

More than two-thirds of people with ADHD have another mental health or learning disorder.
These include:
Because symptoms overlap, a thorough psychiatric assessment is necessary.
For example, difficulty concentrating can be caused by anxiety, depression, or ADHD, or a combination of them.
Diagnosing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder involves more than observing a few restless behaviors.
A qualified psychiatrist will perform a comprehensive psychiatric assessment that may include:
Because attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder looks different across age groups and genders, professional evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Others discover they have ADHD when they come into treatment for their children or when they hear about it from another source.
The following are the symptoms that indicate that you need an ADHD assessment:
These challenges probably exist since childhood, although they might not be officially acknowledged, and they have significant effects on work, relationships, as well as your personal health.
ADHD is a chronic mental disorder. Although it does not limit the potential of the individual. But, with the right therapy and specialist care, individuals with ADHD can be successful in education, career, and social life.
Otherwise, untreated, ADHD may aggravate other risks such as:
Such risks are important to minimize by early diagnosis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and continuous professional support.
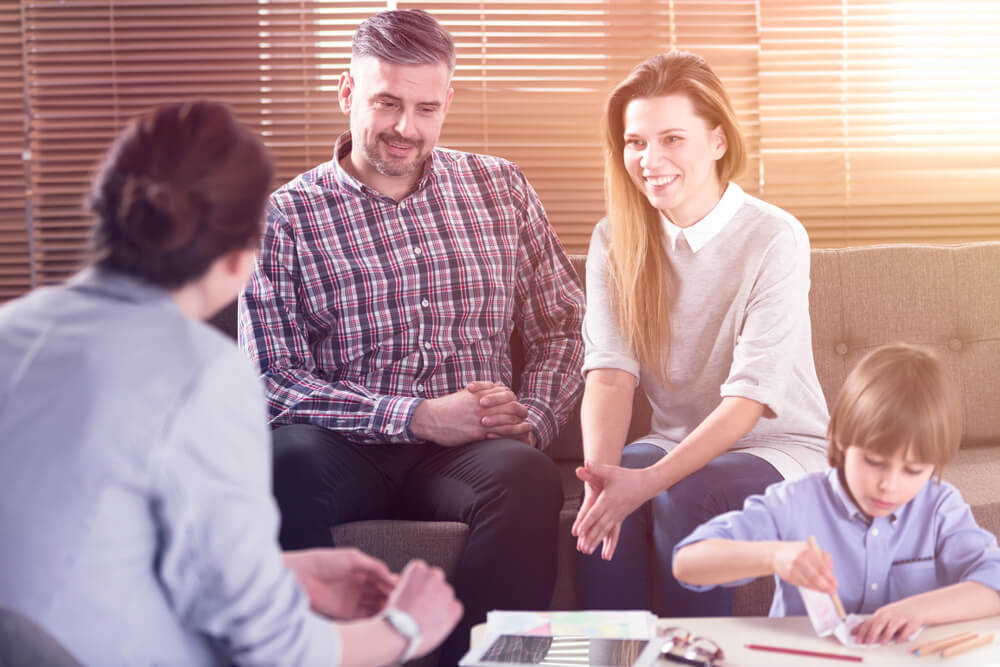

There is no universal treatment for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. The symptoms and needs of every individual are varied. This is the reason why it is highly necessary to seek the assistance of a qualified psychiatrist or mental health provider.
An expert psychiatrist can:
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is not an issue of poor concentration or poor discipline. It is a brain disorder with real neurological differences. While symptoms may disrupt daily life, treatment profoundly transforms things.
Individuals with ADHD can get better with proper management, care, and diagnosis of the condition. In case you are experiencing ADHD or your child has the symptoms, the first thing to do is to seek the assistance of a qualified psychiatric practitioner.
At Health and Psychiatry, our vision is to help patients and families navigate through diagnosis, treatment, and continuing care so that way, ADHD does not pose as an impediment to a happy and healthy life.


Copyright © 2024 Health & Psychiatry, All rights reserved