Depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder affect millions of people worldwide. For many patients, standard treatments such as antidepressants and psychotherapy are not enough. This growing need has led to the widespread adoption of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). It is a non-invasive brain stimulation therapy with a strong clinical backing for treatment-resistant mental health conditions.
Today, several forms of TMS therapy for OCD and depression are available. It includes repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (Deep TMS or dTMS), and Accelerated TMS.
While all aim to restore healthy brain activity. But they differ in technology. Depth of stimulation, treatment duration, and clinical focus.
At Health & Psychiatry, we use NeuroStar® TMS. It is a leading FDA-cleared rTMS system, chosen for its precision, safety profile, and strong evidence base.
Learn about expert Psychiatrist Dr. Dinar Sajan’s approach to TMS Therapy for Treatment-Resistant Depression…
As TMS technology evolves, patients and providers are often faced with a key question:
Should you choose rTMS, Deep TMS, or Accelerated TMS?
Let’s understand each option clearly to help patients make informed decisions.
What Is TMS Therapy?
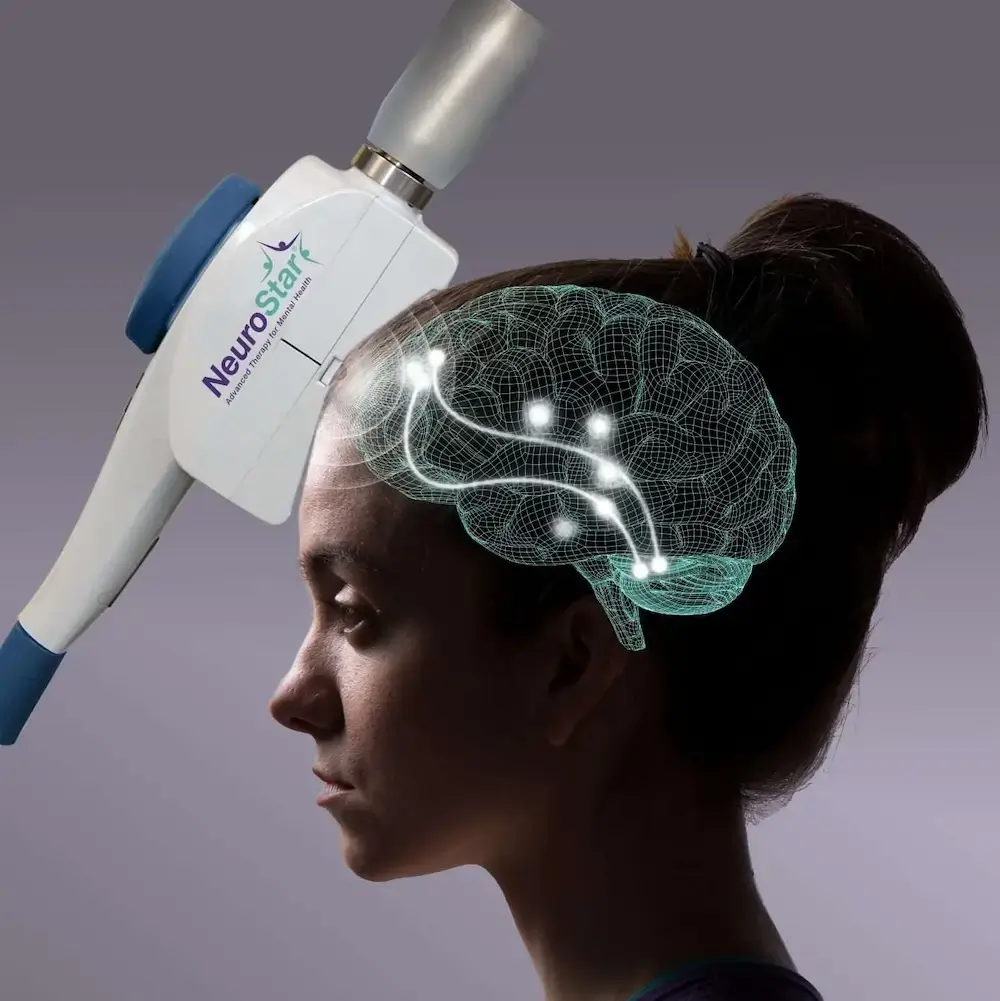
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive neuromodulation therapy. It uses electromagnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain regions involved in mood regulation. Most commonly, the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC).
TMS is FDA-approved for:
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Smoking cessation (specific protocols)
Carlos Peña, Ph.D., M.S., director of the Division of Neurological and Physical Medicine Devices in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, says, “Transcranial magnetic stimulation has shown its potential to help patients suffering from depression and headaches… With today’s marketing authorization, patients with OCD who have not responded to traditional treatments now have another option.”
Large-scale studies show:
- 60-70% response rates in treatment-resistant depression.
- 30- 40% remission rates after a full treatment course.
- Minimal systemic side effects compared to medication.
Unlike medications, TMS does not circulate through the body. Thus making it an attractive option for patients who experience medication intolerance.
→ TMS does not require anesthesia…
→ Does not cause systemic side effects.
→ Allows patients to resume normal activities immediately after sessions…
What is rTMS (Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)?
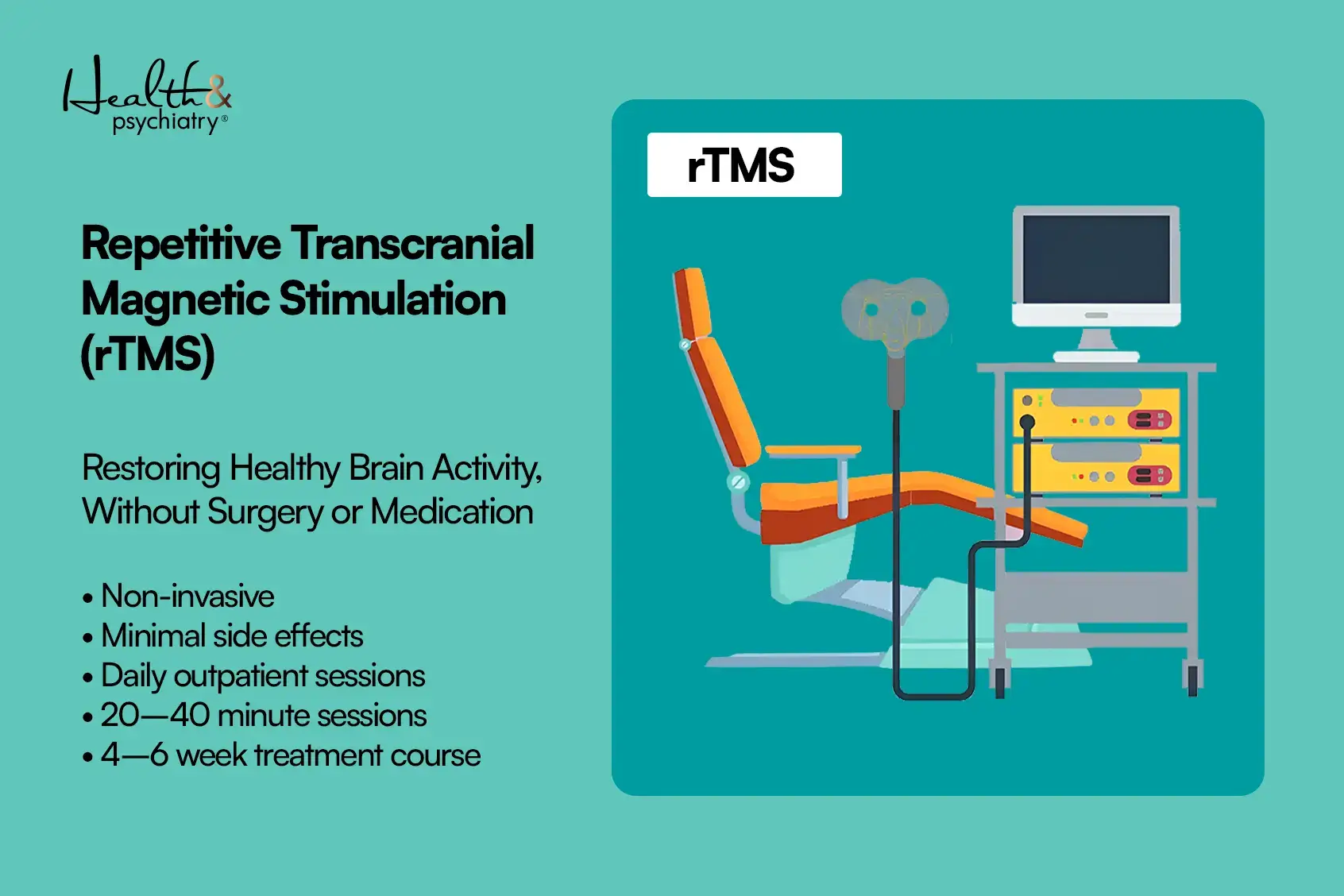
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is the most established and widely researched form of transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy.
It is an FDA-approved non-invasive brain stimulation treatment. It uses repeated magnetic pulses to activate specific areas of the brain involved in mood regulation, particularly regions that tend to be underactive in people with depression.
During rTMS treatment, a magnetic coil is placed against the scalp. There, it delivers controlled repeated electromagnetic pulses at a consistent frequency. These pulses stimulate targeted brain cells without surgery, anesthesia, or systemic medication.
Over time, this stimulation helps restore healthier patterns of brain activity. Leading to a reduction in depressive symptoms.
Key Features of rTMS
- Targets superficial cortical regions.
- Typically delivered once daily.
- Sessions last 20-40 minutes.
- Treatment course: 4-6 weeks.
- FDA-approved since 2008 for depression.
Benefits of rTMS
→ Thousands of clinical trials support this on evidence-based.
→ Offers a high safety profile. With no need for anesthesia or recovery time.
→ Minimal side effects. Most common: mild scalp discomfort or temporary headaches.
→ Well-suited for first-time TMS patients. And those with treatment-resistant depression.
Limitations of rTMS
- Limited depth of stimulation, primarily affecting surface-level brain regions.
- Requires a longer treatment timeline compared to accelerated protocols.
- May be less effective for conditions involving deeper brain circuit dysfunction.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression remains the gold standard starting point for many patients due to its reliability and accessibility.
What Is Deep TMS (Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation)?
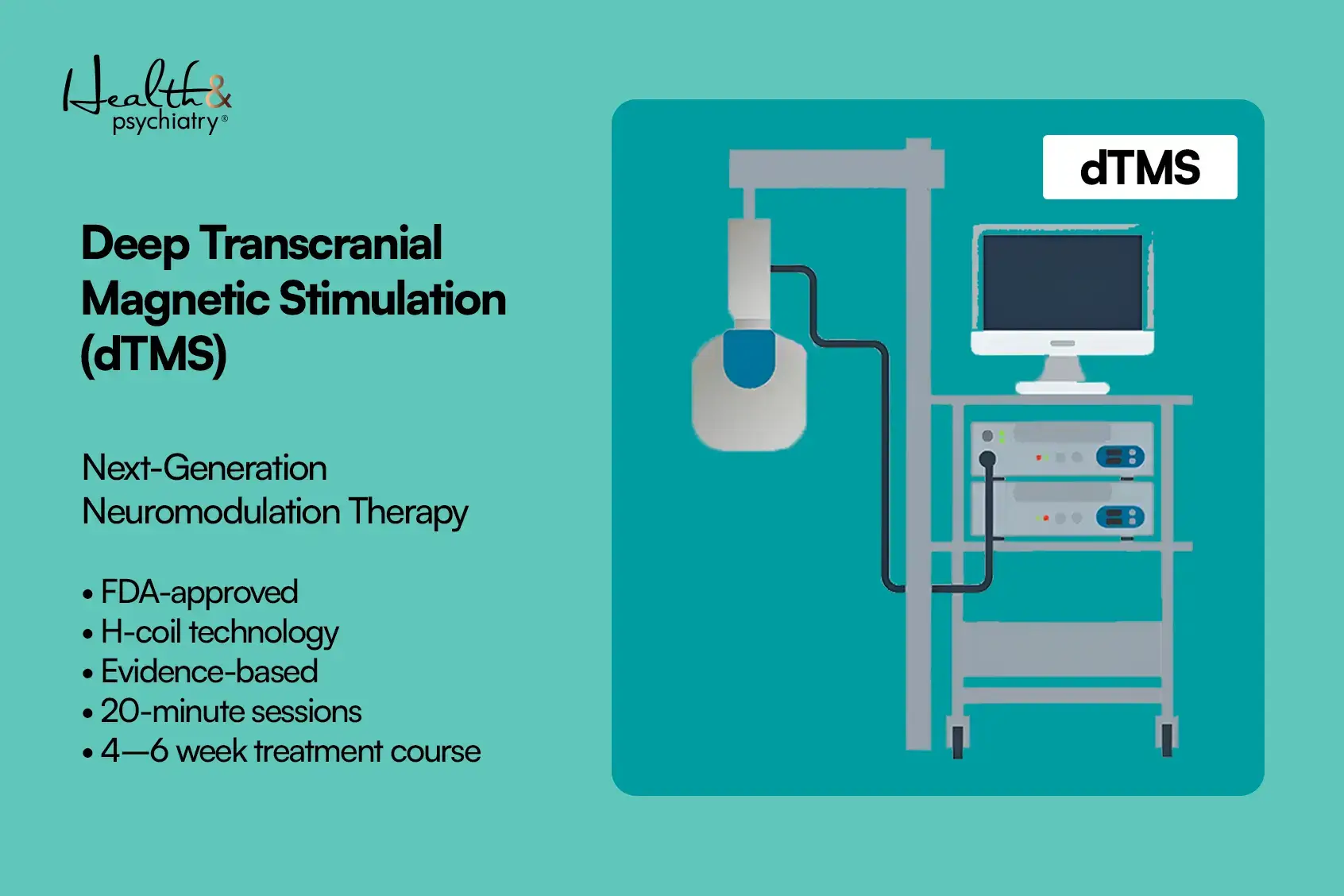
Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (Deep TMS) is an advanced form of TMS therapy. It is designed to stimulate deeper and broader brain regions. Target regions involved in mood regulation and emotional processing.
Like other TMS treatments, deep TMS therapy is non-invasive. It does not require anesthesia. It uses magnetic pulses to help normalize brain activity in areas associated with depression and other mental health conditions.
But how deep does TMS differ from rTMS?
Deep TMS differs from standard rTMS in the design of the magnetic coil. Instead of a traditional figure-8 coil, a specialized H-coil is used in deep TMS therapy. It allows the magnetic field to penetrate deeper into the brain. Reaching areas beyond the surface cortex.
This deeper reach of deep TMS treatment may be beneficial for patients whose symptoms are linked to more complex or widespread neural circuits.
Deep TMS is FDA-approved for major depressive disorder (MDD). And has also been cleared for conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) under specific treatment protocols.
Key Features of Deep TMS
- Stimulates deeper brain structures compared to standard rTMS.
- Uses an H-coil to deliver a broader magnetic field.
- Sessions last approximately 20 minutes.
- Treatment is provided once daily over 4-6 weeks.
- FDA-approved for depression and OCD (protocol-specific).
Benefits of Deep TMS
→ Ability to reach deeper neural networks involved in emotional regulation.
→ May benefit patients with complex or treatment-resistant depression.
→ More effective and higher response rates to rTMS in clinical studies.
→ Non-invasive with no downtime after sessions.
→ FDA awarded deep TMS therapy the Breakthrough status for bipolar depression.
Limitations of Deep TMS
- Some patients experience increased scalp discomfort due to higher intensity.
- Deep TMS machines are noisier. Earplugs are suggested to be used during sessions.
Deep TMS can be an effective option for select patients. Particularly for those who have not achieved sufficient improvement with standard rTMS.
However, the choice between Deep TMS and other TMS modalities should always be guided by clinical evaluation, treatment goals, and according to every patient's needs.
What Is Accelerated TMS?
Accelerated transcranial magnetic stimulation (Accelerated TMS) is an adapted version of TMS intervention. The therapeutic outcomes of the protocol are expected to be achieved within a significantly shorter period of time than the traditional TMS protocols.
Instead of presenting new stimulation technology, Accelerated TMS alters the frequency of the sessions, which could include more than one treatment in a day.
In Accelerated TMS, patients are treated to multiple TMS sessions throughout the day, with theta burst stimulation (TBS) or other high-efficiency protocols.
It is a quick solution as it compresses a typical treatment course of several weeks into one or two weeks. Thus being an attractive alternative to people who require a quicker response to symptoms or otherwise cannot afford more time on a long-term treatment regimen.
The sessions are short, and the average duration of a session is 5 to 10 minutes, with planned intervals between sessions to give the brain time to relax and react to stimulation.
Accelerated TMS is typically given under strict clinical supervision and is mostly only granted to patients with treatment-resistant severe depression or patients who need quick relief.
In recent years, newer accelerated TMS approaches have received FDA clearance. Allowing treatment to be completed in significantly less time.
Two notable examples include:
- SAINT TMS: This method uses individualized MRI-based brain mapping and delivers multiple short TMS sessions each day - typically ten sessions daily across five days. Totaling 50 stimulation sessions within one week.
- BrainsWay SWIFT Deep TMS: This accelerated Deep TMS program is conducted over six consecutive days. With patients receiving five treatment sessions per day. This is followed by a structured continuation phase spanning four weeks. During which two stimulation sessions are provided on a single scheduled day each week.
These protocols are designed to intensify treatment delivery while maintaining safety and clinical oversight, offering a faster pathway to symptom improvement for appropriate patients.
Key Features of Accelerated TMS
- Delivers multiple TMS sessions per day.
- Treatment course completed in a few weeks.
- Sessions are shorter than standard TMS.
- Conducted under enhanced clinical monitoring.
Benefits of Accelerated TMS
→ Faster symptom improvement compared to standard protocols.
→ Reduced overall treatment duration.
→ May be helpful for patients with urgent clinical needs.
→ Early studies report promising response and remission rates.
Limitations of Accelerated TMS
- Not FDA-approved as a standalone treatment protocol.
- Limited long-term research compared to rTMS.
- Requires a full-time commitment during treatment days.
- Not suitable for all patients.
Deep TMS vs rTMS vs Accelerated TMS: Key Differences
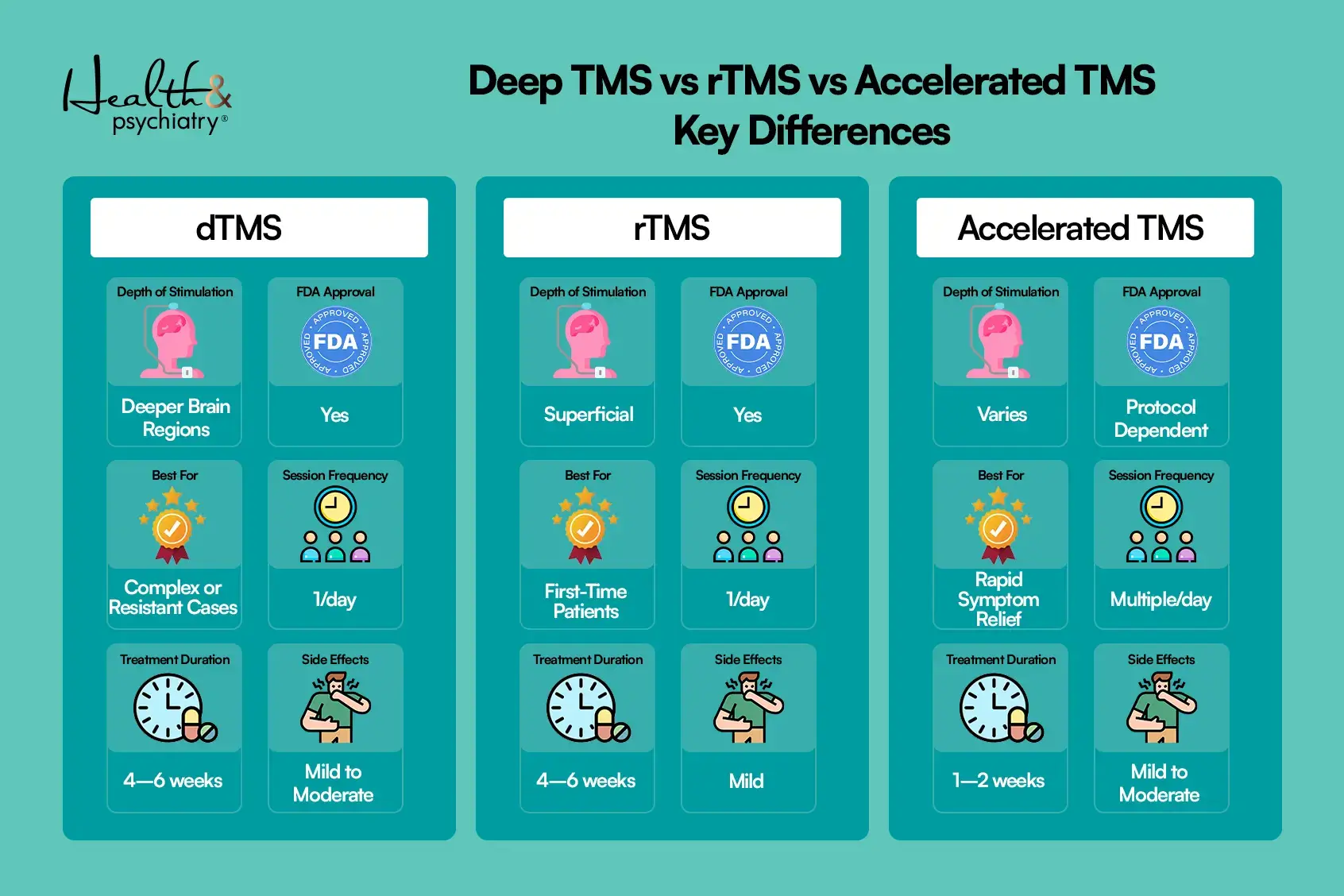
When comparing Deep TMS vs rTMS vs Accelerated TMS, the “best” option depends heavily on patients' clinical needs rather than on one superior technology.
|
Feature |
rTMS |
Deep TMS |
Accelerated TMS |
|
Depth of Stimulation |
Superficial |
Deeper brain regions |
Varies |
|
Session Frequency |
1/day |
1/day |
Multiple/day |
|
Treatment Duration |
4–6 weeks |
4–6 weeks |
1–2 weeks |
|
FDA Approval |
Yes |
Yes |
Protocol-dependent |
|
Best For |
First-time patients |
Complex or resistant cases |
Rapid symptom relief |
|
Side Effects |
Mild |
Mild to moderate |
Mild to moderate |
How Do You Choose the Right TMS Therapy?
Choosing the right TMS treatment should always involve a licensed mental health professional. Key factors include:
- Severity of symptoms
- History of antidepressant response
- Urgency of symptom relief
- Previous TMS experience
- Time availability
- Cost and insurance coverage
Patients with treatment-resistant depression therapy needs may benefit more from Deep TMS or Accelerated TMS, while others respond well to standard rTMS.
Get TMS Therapy in Florida Under Expert Clinical Supervision at Healt & Psychiatry!
In Health and Psychiatry, TMS treatment is provided under the very experienced medical supervision, conducted under safe, accurate, and individual care throughout the treatment.
Dr. Sajan Dinar, MD. heads our treatments and a highly trained clinical team with vast experience in neuromodulation and mental health care support our treatments.
We use NeuroStar® TMS, a high-ranking FDA-approved device with high accuracy and comfort rate, as well as high efficacy in the treatment of depression.
Every treatment plan is individually designed and closely monitored to achieve the best results and comfort of the patient through the treatment process.
Looking for a reliable TMS therapy in Florida, conducted by professionals who value clinical excellence and patient welfare? Health and Psychiatry is the right place to be.
Schedule your appointment NOW, for a better mental health, for Hope, Health & Harmony!
FAQs
What is repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation?
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a non-invasive therapy that uses repeated magnetic pulses to stimulate specific brain areas involved in mood regulation.
Which TMS therapy is the most effective?
Effectiveness varies by individual. rTMS has the strongest evidence base, Deep TMS may help more complex cases, and Accelerated TMS offers faster results for selected patients.
Is Deep TMS better than rTMS?
Deep TMS is not universally better but may be more effective for patients who need deeper brain stimulation or have not responded to rTMS.
Is Accelerated TMS FDA-approved?
The individual TMS devices are FDA-approved, but accelerated protocols are still considered emerging and are typically offered under specialized clinical supervision.




